Centered Log-Ratio Transformation¶
The Centered Log-Ratio (CLR) Transformation is a normalization technique used for compositional data, where values represent relative proportions of a whole rather than absolute quantities. It helps remove the closure effect, a mathematical constraint where components of a dataset sum to a fixed total (e.g., 100%), which can distort statistical analysis. The transformation converts compositional data into an unconstrained space, making it suitable for methods that assume independent variables.
As an example, in geochemistry, elemental concentrations in rocks are often expressed as proportions (e.g., major oxides summing to 100%). Directly applying statistical models to such data can lead to misleading results due to spurious correlations. The CLR transformation ensures that geochemical variables are properly normalized, allowing for more accurate pattern recognition, clustering, and geostatistical modeling. It is particularly useful for identifying geochemical trends in exploration, such as distinguishing between hydrothermal alteration zones and background compositions.
Warning
The input data must be in the same unit (e.g., percent) to ensure meaningful results. Additionally, if all points contain one no-data value, CLR cannot be performed. The method requires at least 2 properties.
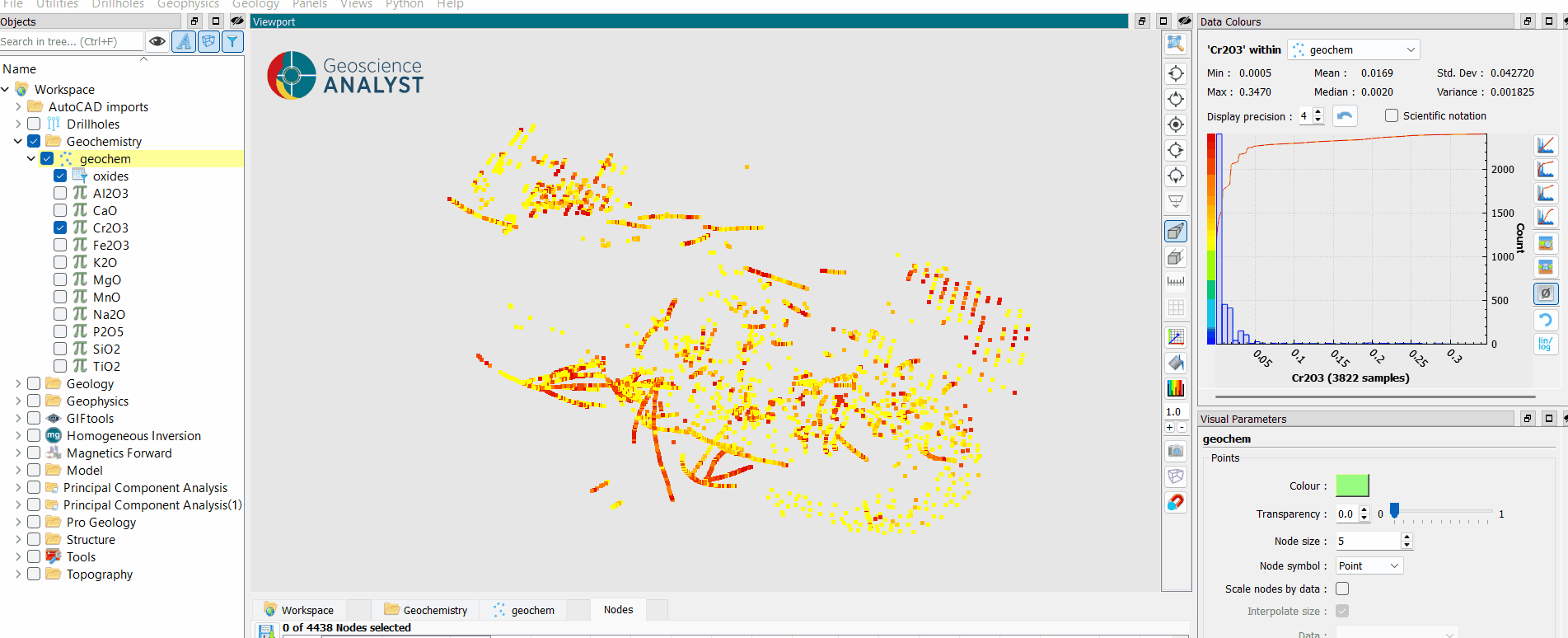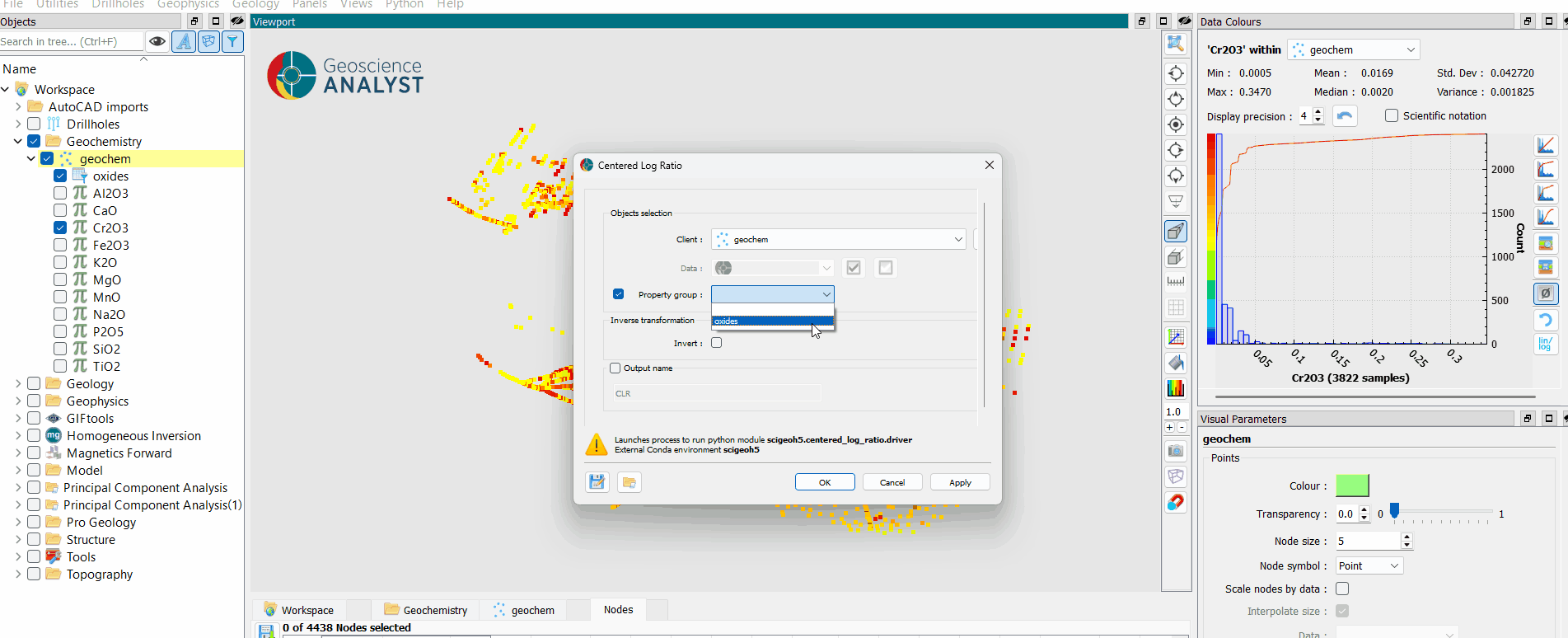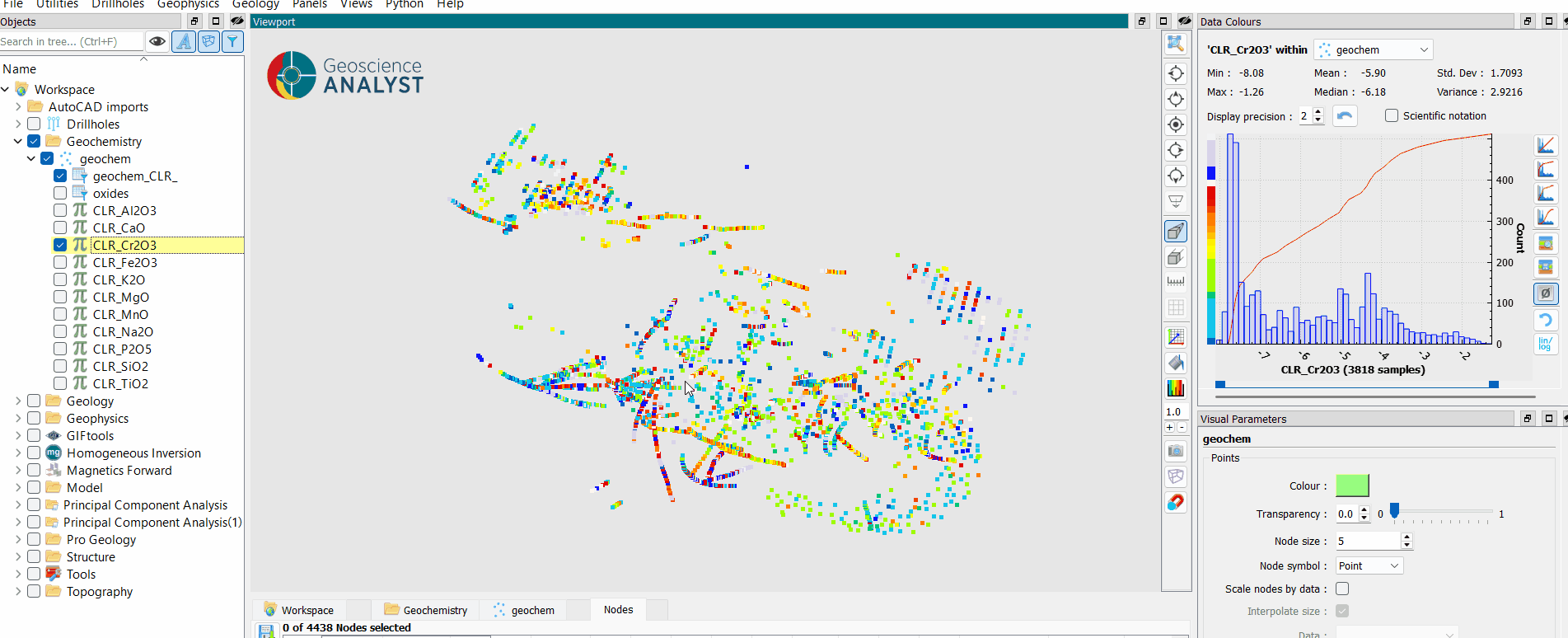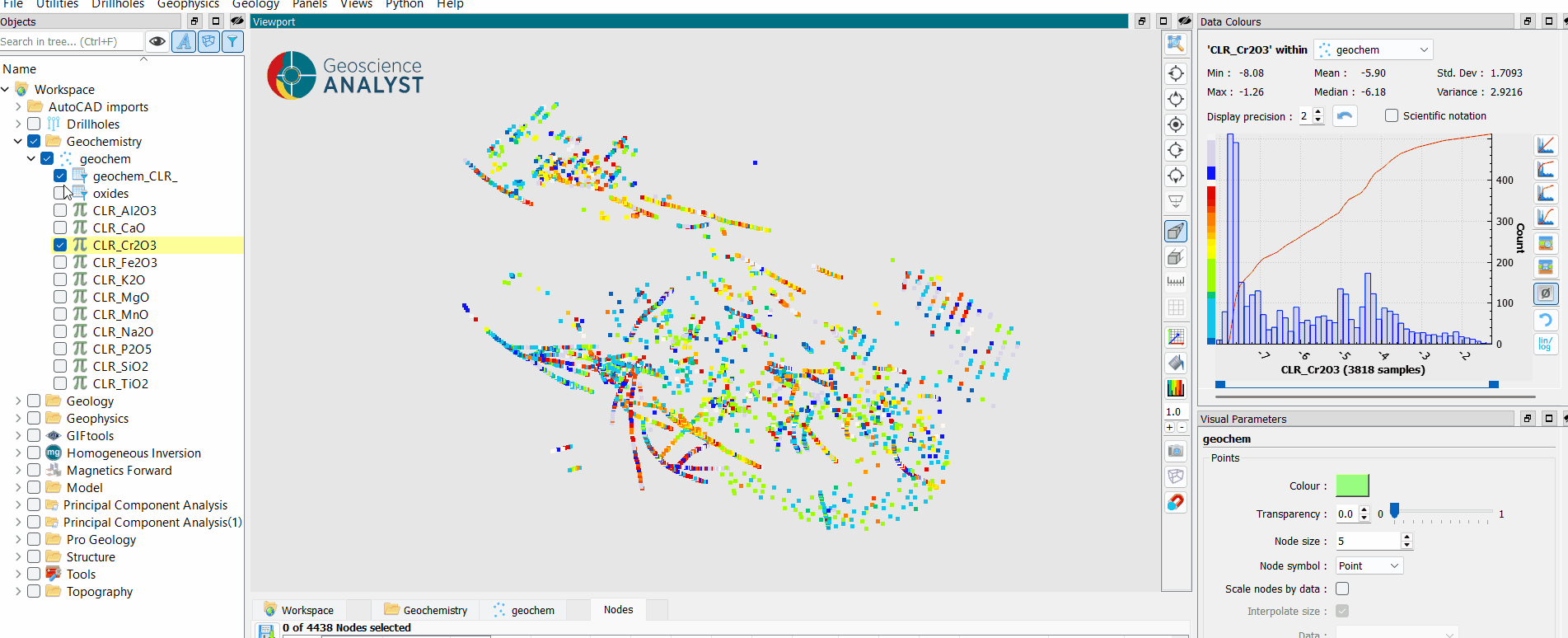
Interface¶
The general parameters controlling the Centered Log-Ratio (CLR) Transformation are shown in the figure below.
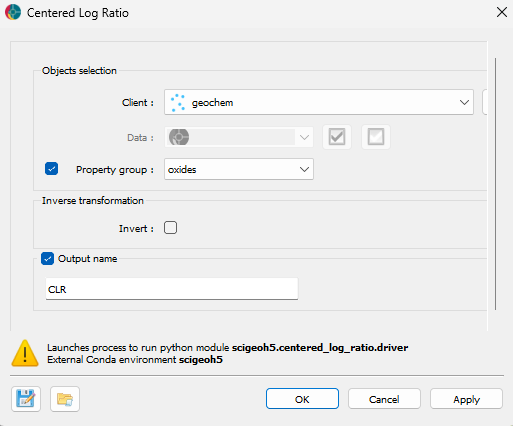
The options are described as follows:
Object: The object containing the dataset to be transformed using the CLR method.
Data: The geochemical or compositional data to be transformed. Users can select multiple Float data properties to apply the transformation.
Inverse transformation: Enables the inverse CLR transformation, converting CLR-transformed data back to compositional data that sums to 1. This is useful for reverting processed data while preserving the compositional nature, though the original scale is lost.
Prefix: Prefix for the data in the output data group; will be added as ‘[prefix]_[data name]’.
Output data group name: Name for the resulting data group with the centered log ratio.
Once the parameters are selected, press OK to run the transformation.
Tutorial¶
The following animated image presents a tutorial on how to use the CLR application.
Open the application.
Select the object containing the data.
Select the data to be analyzed.
(optional) Choose to do the inverse transformation.
(optional) Choose the name of the output results.
Run the application.
Inspect the transformed data.